The Active House
We often talk about passive houses and only rarely about active houses. Yet, the Active House is also a construction protocol that aims to prioritize sustainability and comfort, with the further goal of generating a positive impact on the surrounding environment. The active house is a healthy and, above all, sustainable home: respecting the standards of the protocol requires building while preserving the balances of the global climate, creating a cleaner, healthier, and safer world.
Reduced consumption, minimal heat dispersion, triple-glazed windows, high air tightness, and air exchange in a maximum of 3 hours are just some of the parameters that contribute to making a building a passive house.
FEATURES OF THE ACTIVE HOUSE
Renewable energy, minimal environmental impact, sustainable materials: those who live in an active house are attentive to their own well-being, but also to the future of the world in which they live. The fundamental principles of this construction protocol focus on:
Living comfort
which is defined by evaluating two parameters:
-
the amount of natural light, direct or indirect
-
the quality of the internal air.
The goal is to recreate the characteristics of the external environment in the internal one. To live better.
L’obiettivo è di ricreare nell’ambiente interno le caratteristiche proprie di quello esterno. Per vivere meglio.
Energy efficiency
through the use of integrated systems that use renewable sources, we are committed to minimizing the energy needs coming from external sources.
Positive impact on the environment
The Active House is built with ecological and sustainable materials, which have a very low impact on the environment.
Fixtures
In an active house, the window and door frames also have high energy efficiency: they maximize the insulation of the rooms and allow solar radiation to heat them
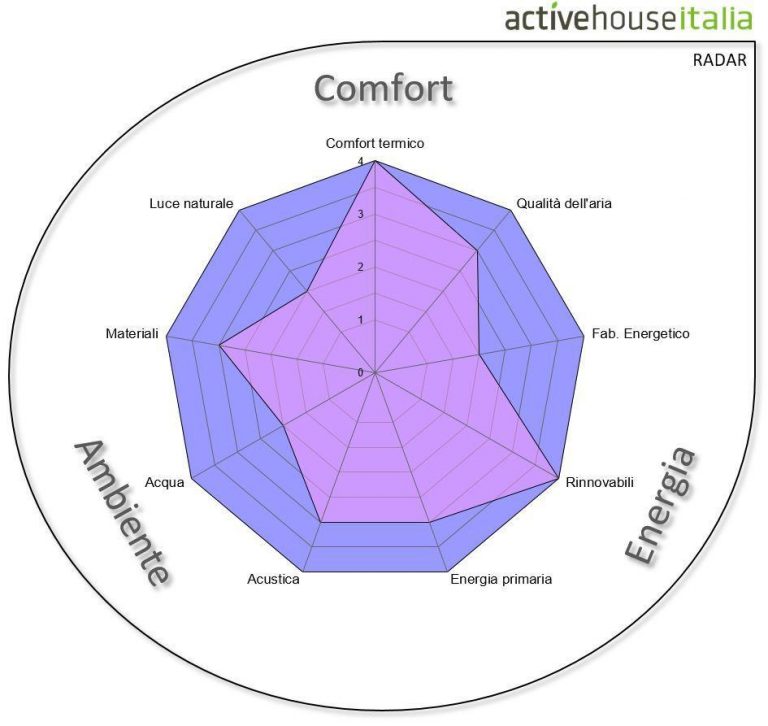
Radar Model
To obtain active house certification, the building is evaluated according to various parameters, which are represented in a model called "radar," of which we have an example here.
On the different sides of the radar are the items that define:
LIVING COMFORT:
related to the presence of natural light, internal temperature, air quality, and acoustic insulation;
SUSTAINABILITY
:
a parameter that can be evaluated based on water use and emissions
ENERGY EFFICIENCY
:
here we consider the environmental impact, the supply chain, and the energy needs.
In conclusion, the radar is a kind of photograph of the level achieved, the figurative result of the overall judgment given to the property. Each building, therefore, will have its own radar, with a specific shape: the more developed the radar is at each level, the more performing the building will be in terms of energy output.
Let’s give some examples of the parameters that are evaluated:
- the wood used must come from FSC or PEFC certified forests;
- construction materials are analyzed considering both the production processes and disposal after 50 years;
- air quality derives from the use of a ventilation system, etc.
A score is assigned to each of the above items and the house is certified as an Active House only if each parameter has obtained a minimum of 4 points



